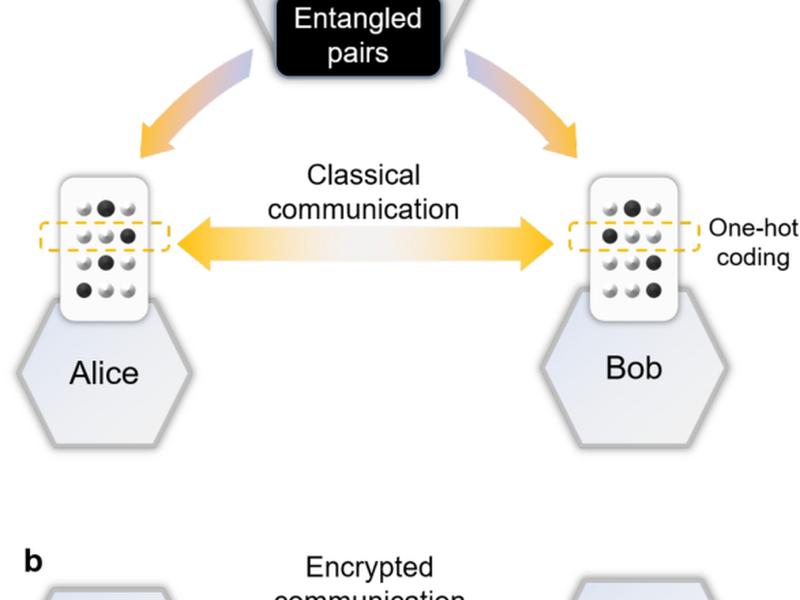
This article proposes a quantum oblivious transfer (QOT) protocol that is applicable to commercially available quantum infrastructures with limited fidelity and quantum capacity, and provides a theoretical security guarantee. The protocol is based on a three-party model where any party can be dishonest, but the third party cannot collude with the communicating parties. The effectiveness of the proposed approach is demonstrated through extensive experiments on the IBMQ quantum computer and quantum simulators with several DNN models for different tasks, including general image and medical image classifications.