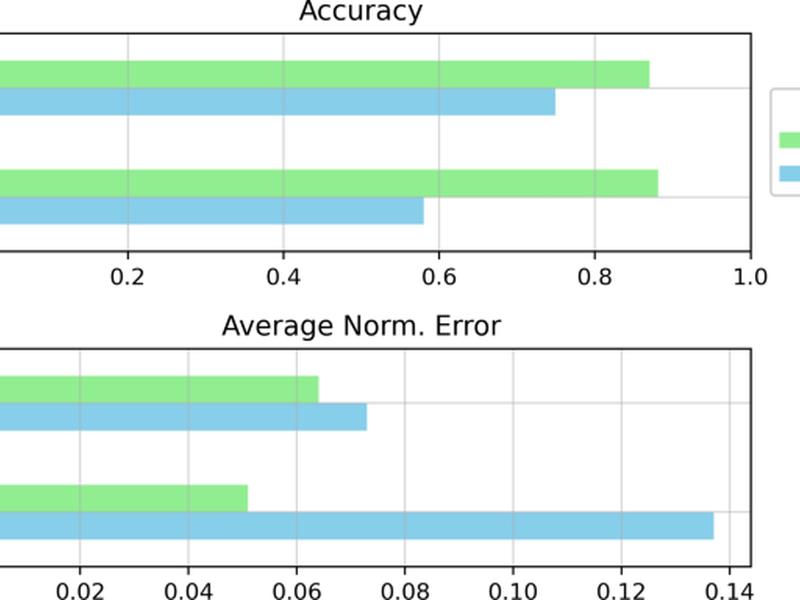
This article discusses a simulation method for creating training data for deep learning models in the field of medical diagnosis. The method expands upon a previously proposed synthetic dataset and allows for random sampling of mixture distribution parameters while maintaining real-world fidelity. The article highlights the advantages of using synthetic datasets for training and evaluating indirect methods in the medical field.