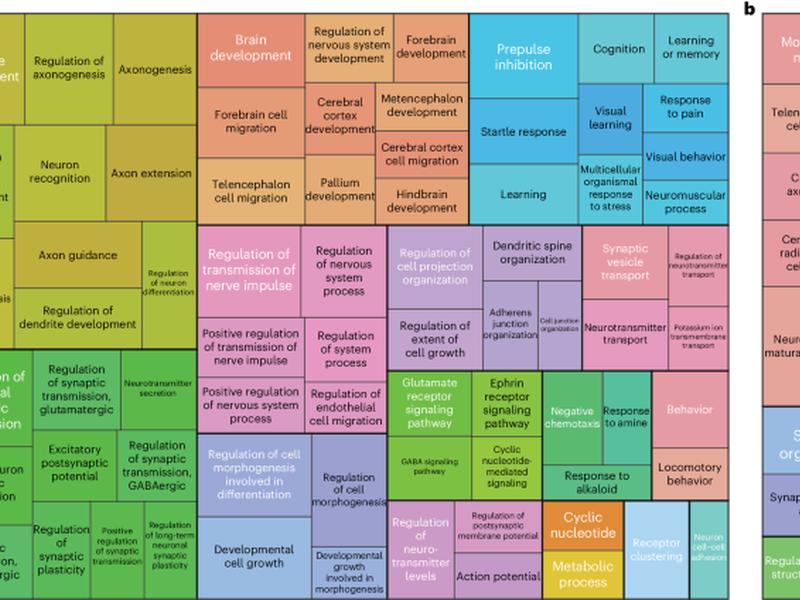
This article discusses a genome-wide association meta-analysis (GWAMA) of three independent GWAS for Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS). The study integrated multiple layers of functional omics data to identify pathways and cell types relevant to RLS, and also included sex-stratified GWAS and a genetic investigation of the X chromosome. The results of the study could potentially lead to improved risk prediction and identification of drug targets for RLS.