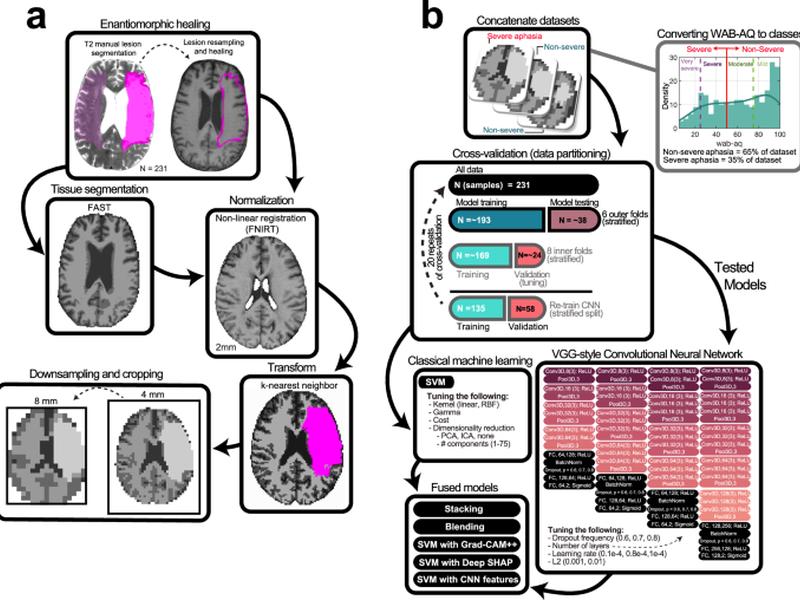
This article discusses the use of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) in predicting aphasia severity following stroke. The results show that CNNs achieve higher predictive accuracy than traditional machine learning methods by leveraging more distributed morphometry patterns. The study also highlights the potential of CNNs in advancing our understanding of stroke and its effects on the brain.