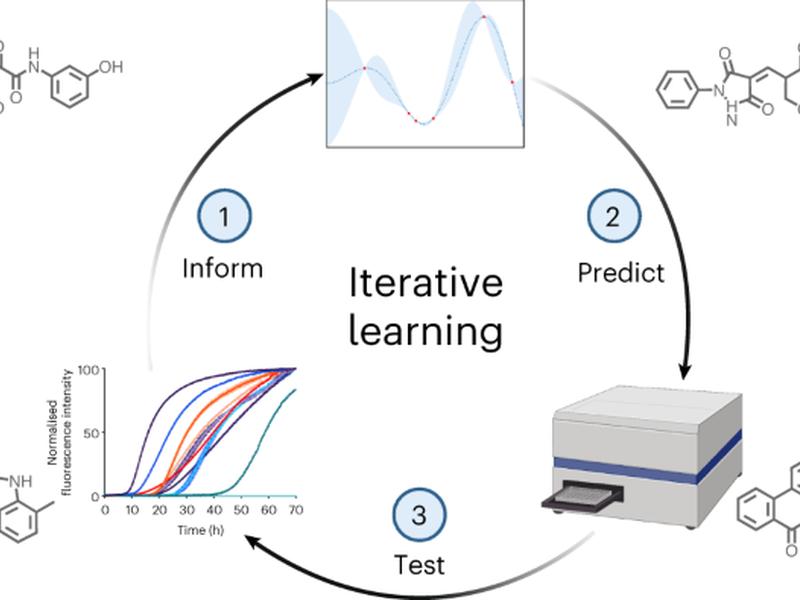
This article discusses a machine learning approach to identifying and optimizing compounds with high potency in inhibiting the surface-catalyzed secondary nucleation step in the aggregation of αS. The approach uses a chemical kinetics assay, a variational autoencoder, and a random forest regressor to train and predict the potency of compounds.