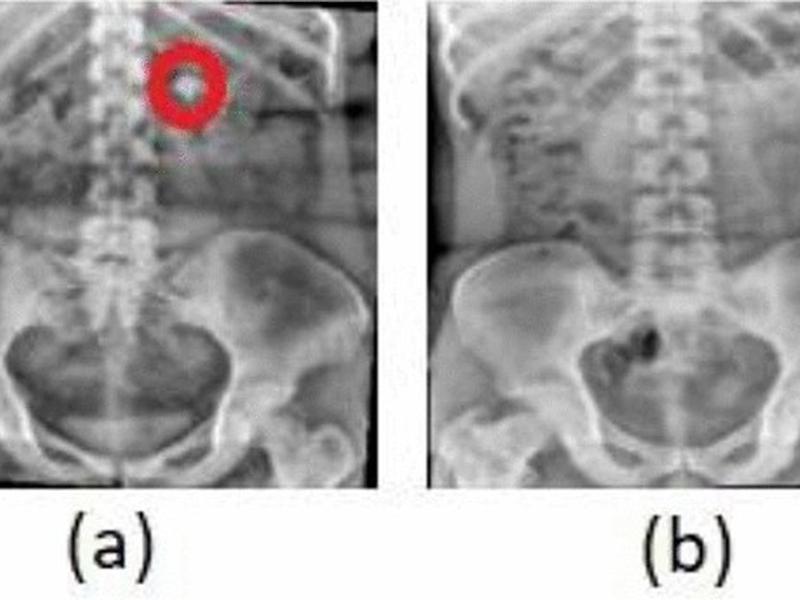
This article discusses the use of transfer learning and explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) to accurately classify kidney-ureter-bladder (KUB) X-ray images as either normal or containing kidney stones. The results show that the model achieves a testing accuracy of 97.41% and the incorporation of XAI techniques increases fairness and transparency in the decision-making process. This can aid doctors in accurately identifying kidney stones and implementing effective treatment strategies.