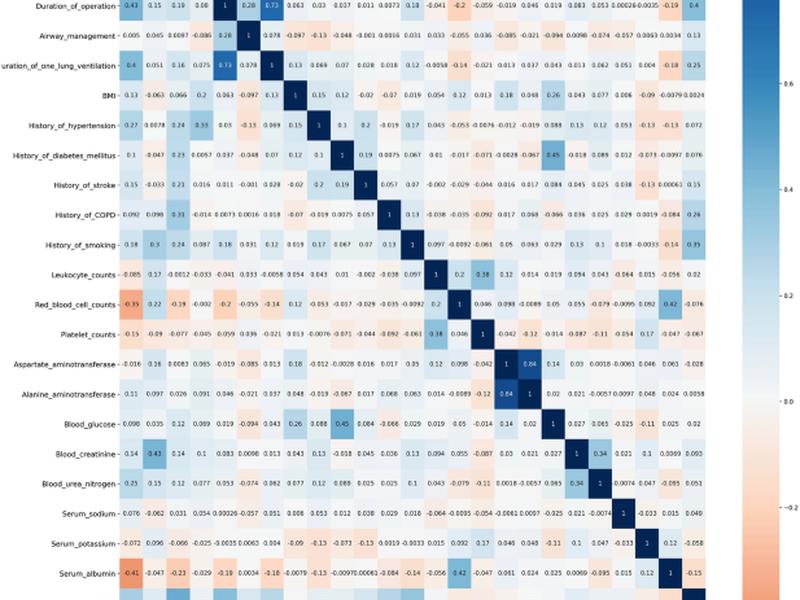
This study aimed to construct an early prediction model for postoperative pulmonary complications (PPCs) after thoracoscopic surgery using machine learning and deep learning algorithms. The study analyzed data from 905 patients who had undergone thoracoscopic surgery and collected demographic and clinical variables, preoperative laboratory tests, and information on surgery and anesthetic management. The study focused on PPCs, which include respiratory infection, respiratory failure, pleural effusion, pulmonary atelectasis, pneumothorax, bronchospasm, and aspiration pneumonia.