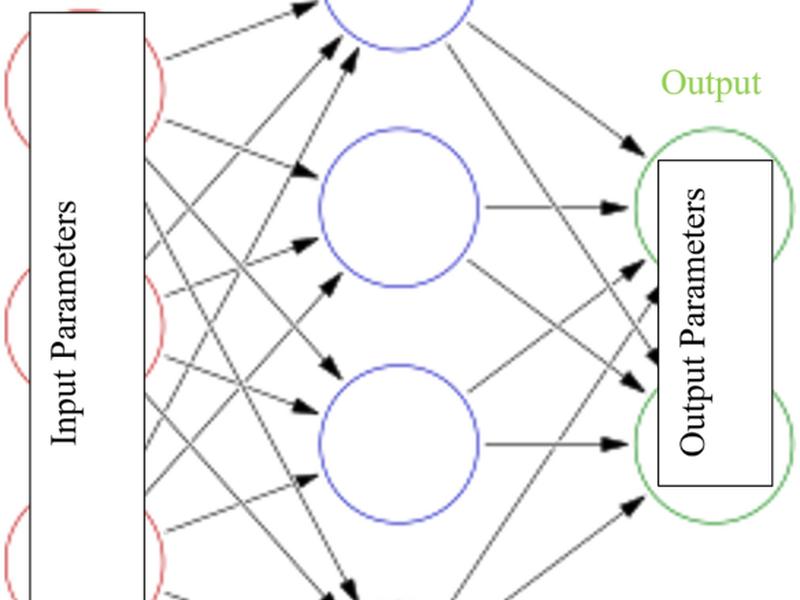
This study proposes the use of machine learning (ML) tools such as artificial neural networks (ANN), support vector machines (SVM), and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference systems (ANFIS) to estimate the contact angle, a key indicator of shale wettability, providing a more efficient alternative to conventional laboratory methods. Initial data analysis showed that the elements affecting the shale wettability are primarily reliant on the pressure and temperature at which it operates, the total organic content (TOC), and the mineral composition of the rock. The ANN model performed the best, achieving a training R2 of 0.99, testing R2 of 0.98 and a validation R2 of 0.96, with an RMSE below 5. An empirical correlation was developed based on the optimized weights and biases obtained from the ANN model to predict contact angle values.