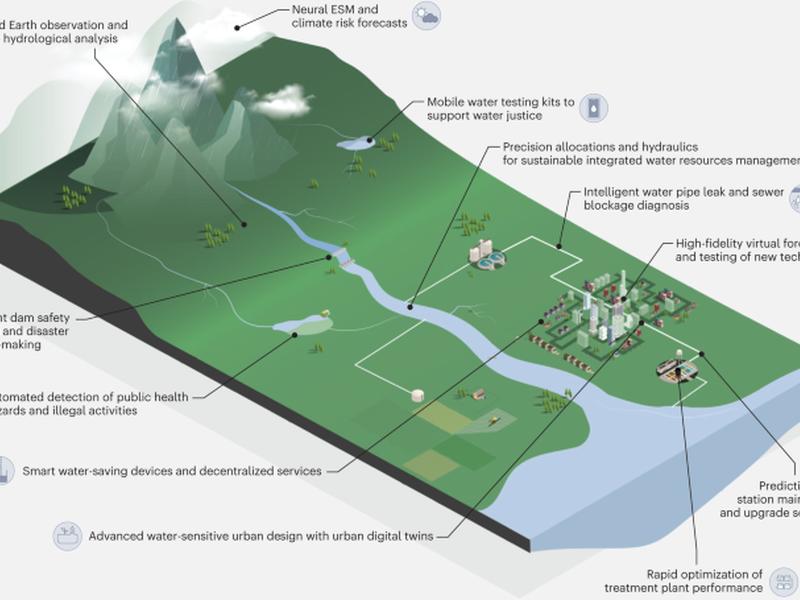
AI is a machine-based ‘intelligent agent’ that can interact with its environment and autonomously take actions to achieve goal-oriented outcomes. ML is a subset of algorithmic models that learn and predict outcomes through passive observation of the environment. AI applications can be used to improve water supply, distribution and disposal, as well as demand management and water justice. AI can also be used to simulate, inform and optimize operating policy for whole water systems. ML models can process big datasets to provide precise quantitative estimates of historical freshwater location and persistence, aiding forensic identification of water stress and scarcity drivers.