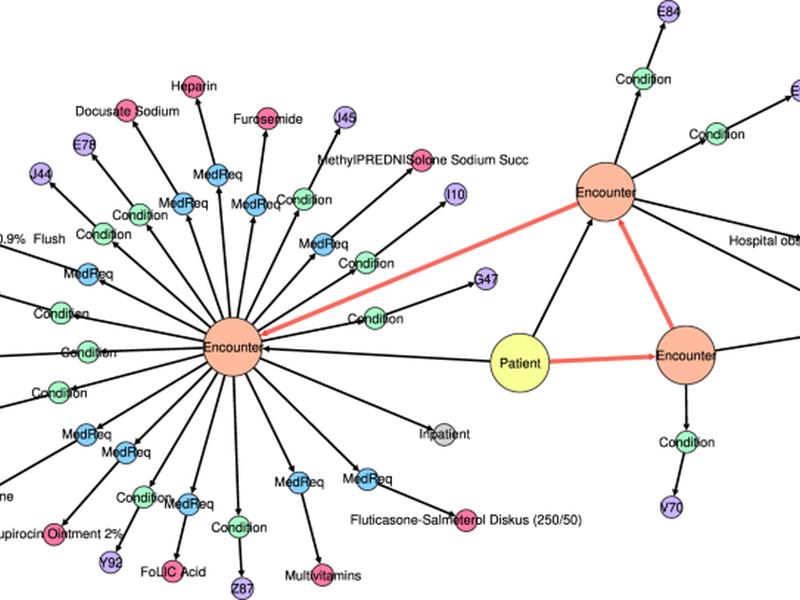
This paper presents a machine-learning algorithm for generating electronic healthcare records represented as sequential graphs (patient trajectories). The algorithm, called VGAE, is tailored to patient trajectories and is capable of generating novel large-scale samples. The numerical experiments were conducted using the Medical Information Mart for Intensive Care (MIMIC-IV) database, which provides critical care data for thousands of patients admitted to the intensive care units at the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center. The patient, visit, diagnosis, and medication data tables were migrated to a labeled property graph (LPG) database, which follows the FHIR standard for healthcare data.