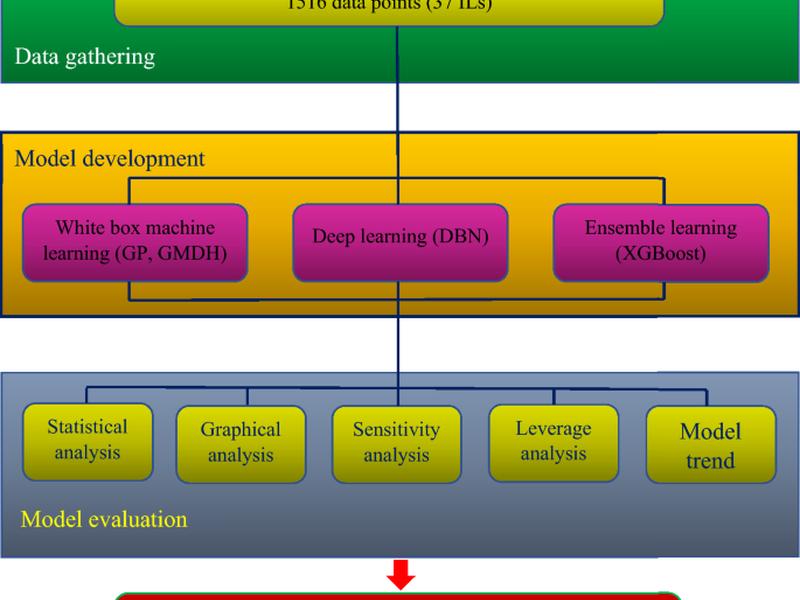
This article discusses the use of machine learning techniques to determine the solubility of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) in ionic liquids (ILs). Seven input variables, including temperature (T), pressure (P), two critical variables such as temperature (Tc) and pressure (Pc), acentric factor (ω), boiling temperature (Tb), and molecular weight (Mw), were used in the models. The findings show that the XGBoost model provides more precise calculations for H2S solubility in ILs, with an average absolute percent relative error (AAPRE) of 1.14%, root mean square error (RMSE) of 0.002, standard deviation (SD) of 0.01, and a determination coefficient (R2) of 0.99. The sensitivity assessment demonstrated that temperature and pressure had the highest negative and highest positive affect on the H2S solubility in ILs, respectively.