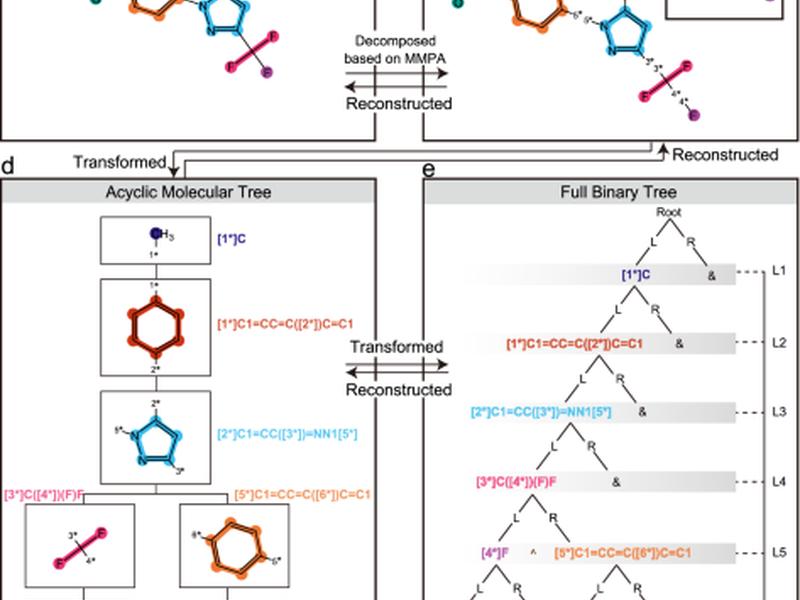
The t-SMILES family of models has shown potential in generating highly novel molecules with 100% theoretical validity and improved performance on low-resource datasets. These models are proficient in capturing physicochemical properties and have shown benefits over existing baseline models in goal-oriented tasks. Various singleton and hybrid strategies can be used in the t-SMILES family, and rigorous comparative experiments have been conducted to assess their performance. The training data includes essential information for designing efficient d.