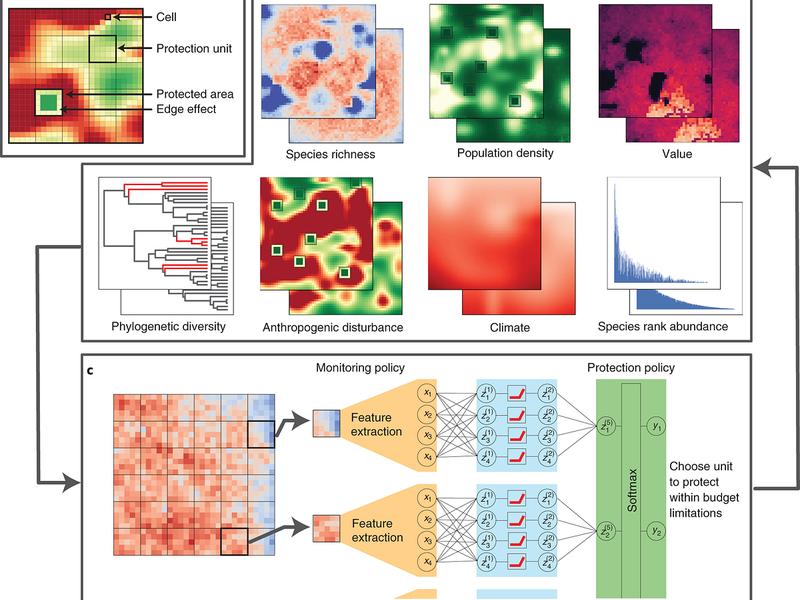
This article explores the use of deep learning, a subset of artificial intelligence, to estimate global biodiversity patterns. By leveraging neural networks and vast amounts of ecological data, researchers can produce high-resolution maps of biodiversity that can inform conservation efforts and policymaking. Deep learning has the potential to revolutionize biodiversity research by providing more reliable and detailed insights into the distribution of species.