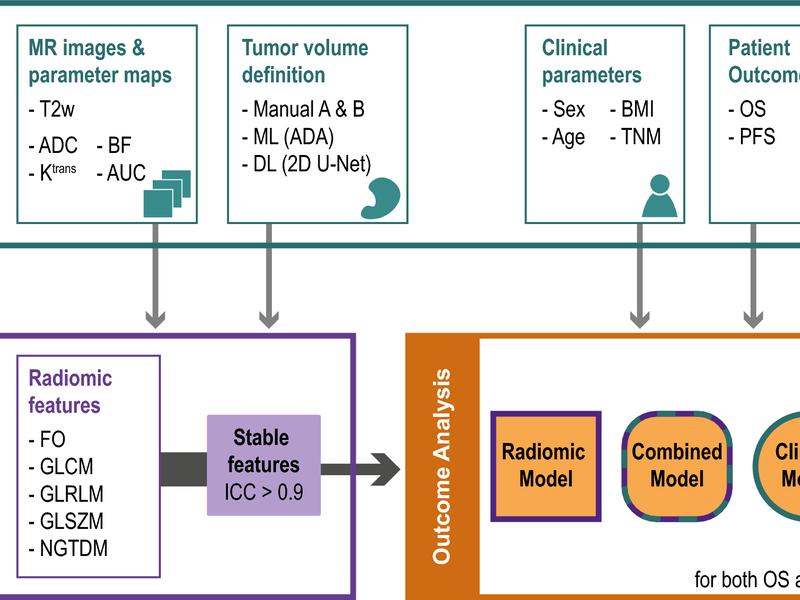
This study investigated the stability of MRI-based radiomics features in a rectal cancer cohort of 81 patients when generating features from both anatomical MRI and qMRI, using three different methods to define the tumor volume. The prognostic value of the identified stable radiomics features was also evaluated by assessing the features’ association to the patients’ 5-year progression-free survival and overall survival. A flowchart detailing the input of MRI parameters and tumor volumes to the radiomics model as well as how radiomics features were extracted and used in outcome analysis together with clinical parameters was provided. The study was conducted in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration and approval was obtained from the Institutional Review Board and the Regional Committee for Medical and Health Research Ethics.