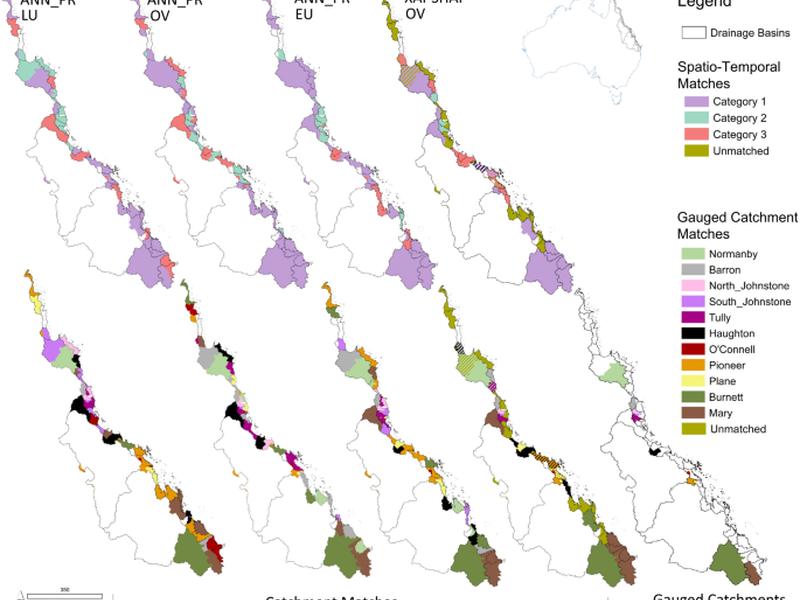
This article discusses the use of proxy spatial data to classify ungauged catchments with similar Dissolved Inorganic Nitrogen (DIN) responses. A neural network pattern recognition model (ANN-PR) and explainable artificial intelligence approach (SHAP-XAI) were used to match all ungauged catchments that flow to the Great Barrier Reef to gauged ones. The suitability of the catchment matches was verified using a neural network water quality (ANN-WQ) simulator trained on gauged catchment datasets. The results showed that discriminating training data to DIN regime benefits ANN-WQ simulation performance in unsupervised scenarios. Priority monitoring areas were identified to gain observed data for all DIN regimes in catchments that flow to the Great Barrier Reef, Australia.