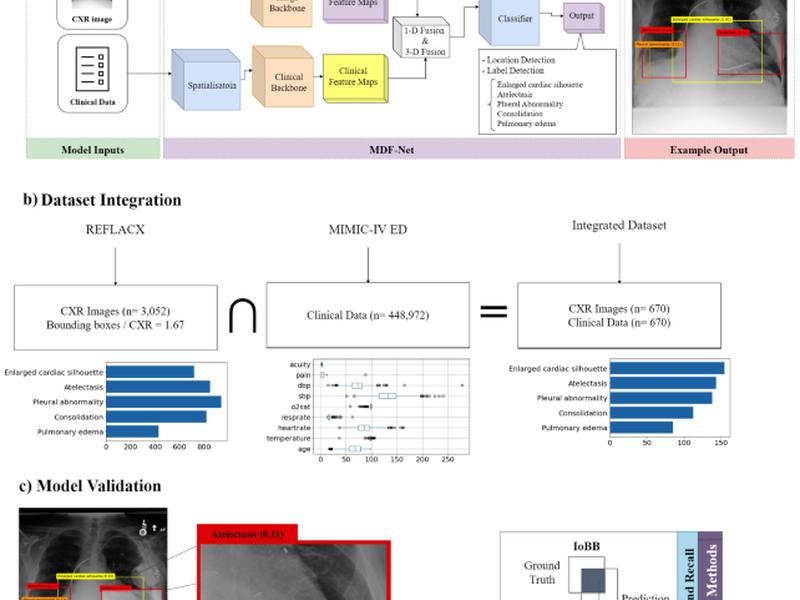
This study investigates the effects of including patients’ clinical information on the performance of deep learning (DL) classifiers for disease location in chest X-ray images. A novel architecture consisting of two fusion methods is proposed to enable the model to simultaneously process patients’ clinical data (structured data) and chest X-rays (image data). Results show that incorporating patients’ clinical data in a DL model together with the proposed fusion methods improves the disease localization in chest X-rays by 12% in terms of Average Precision compared to a standard Mask R-CNN using chest X-rays alone. Ablation studies also emphasize the importance of multimodal DL architectures and the incorporation of patients’ clinical data in disease localization.