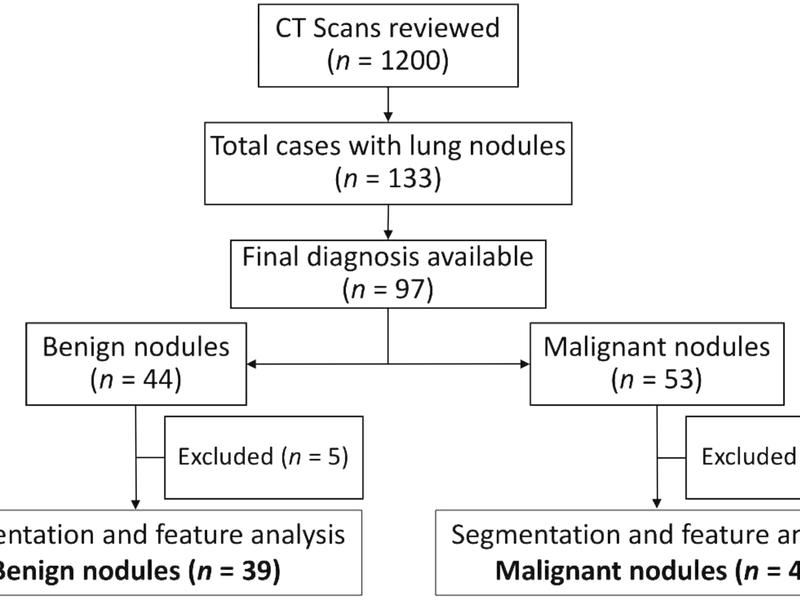
This observational study assessed the utility of radiomics in differentiating between benign and malignant lung nodules detected on computed tomography (CT) scans. Employing random forest feature selection, the study identified ten important radiomic features for distinguishing between benign and malignant nodules. The Decision Tree model demonstrated superior performance, achieving 79% accuracy, 75% sensitivity, 85% specificity, 82% precision, and 90% F1 score. The implementation of the XGBoost algorithm further enhanced these results, yielding 89% accuracy, 89% sensitivity, 89% precision, and an F1 score of 89%, alongside a specificity of 85%. The study establishes radiomics as a powerful, non-invasive adjunct to CT scans in the differentiation of lung nodules, with significant implications for clinical decision-making.