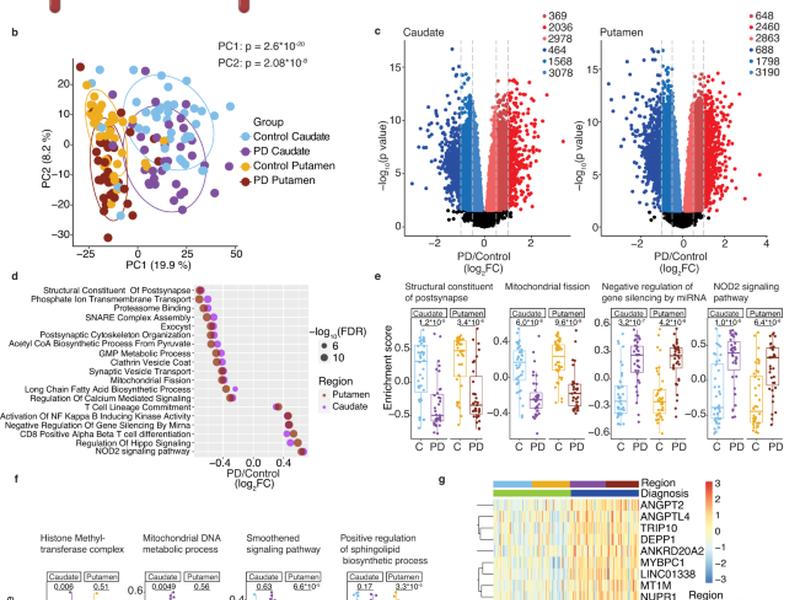
This study used bulk RNA-seq to analyze the molecular pathways dysregulated in the caudate and putamen of Parkinson’s Disease (PD) patients compared to control donors. Principal component analysis (PCA) revealed two significant clusters, corresponding to the striatal region and clinical diagnosis. Differential gene expression analysis revealed 5383 and 5110 up and downregulated RNAs, respectively, in the PD caudate compared to controls, and 5971 and 5676 up and downregulated RNAs, respectively, in PD putamen compared to controls. Gene set variation analysis (GSVA) revealed decreases in transcripts encoding proteins involved at the synapse, such as postsynaptic membrane, vesicular and ion transport, and calcium-mediated signaling, as well as other transcripts downregulated in the PD caudate and putamen encoding proteins involved in lipid metabolism and mitochondrial fission.