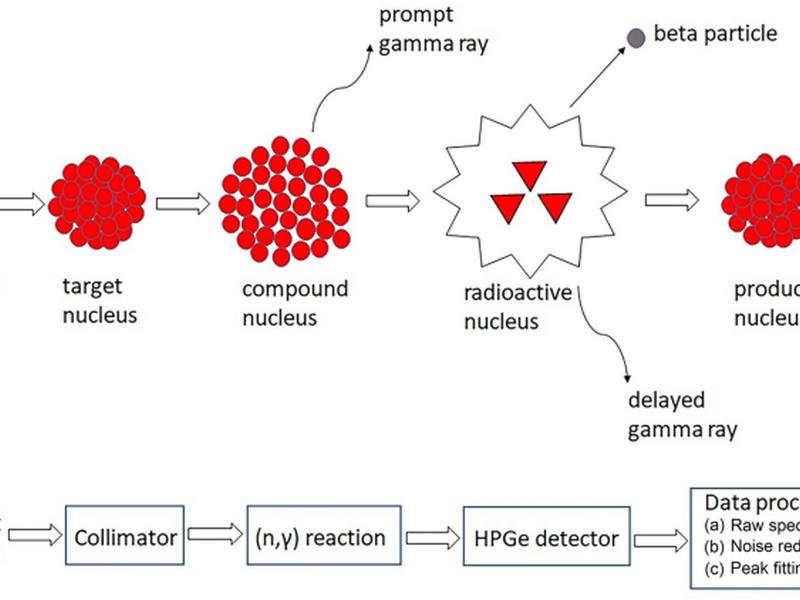
This article discusses the use of neutron-capture prompt-gamma activation analysis (PGAA) for the detection of illicit radiological materials. Six different machine-learning algorithms were developed to classify radioactive elements based on the PGAA energy spectra. The model performance was evaluated using standard classification metrics and trend curves with an emphasis on comparing the effectiveness of algorithms that are best suited for classifying imbalanced datasets. The tree-based algorithms (Decision Trees, Random Forest and AdaBoost) have consistently outperformed Support Vector Machine and K-Nearest Neighbours. AdaBoost was found to be the preferred classifier to analyse data containing PGAA spectral information due to the high recall and minimal false negatives reported in the minority class.
Previous ArticleUs Firm Sutherland In Talks To Buy Ites Platform Suneratech
Next Article 5 Compliance Automation Trends To Watch In 2023