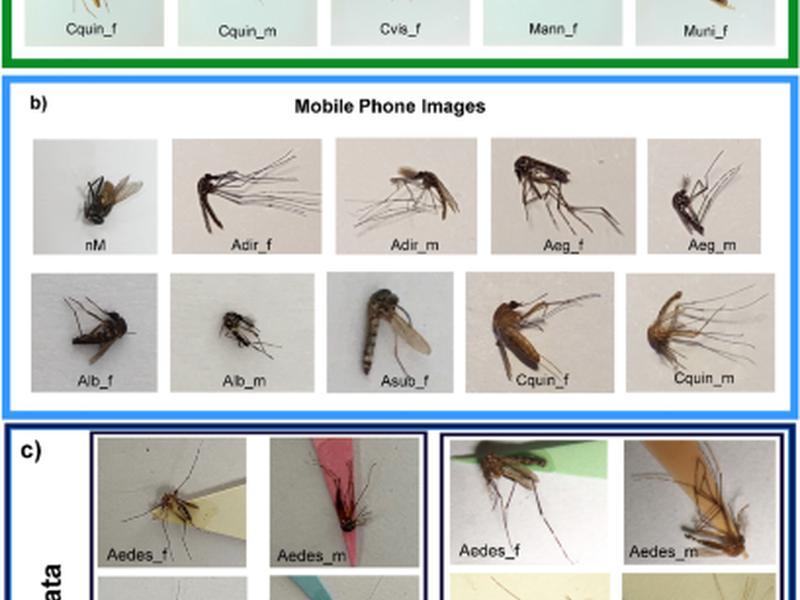
Mosquito-borne diseases such as dengue fever and malaria are the top 10 leading causes of death in low-income countries. Control measure for the mosquito population plays an essential role in the fight against the disease. Currently, several intervention strategies; chemical-, biological-, mechanical- and environmental methods remain under development and need further improvement in their effectiveness. This study proposed an automatic screening, namely the deep metric learning approach and its inference under the image-retrieval process with Euclidean distance-based similarity. The model was developed using ResNet34 and tested with both image sources: stereomicroscope and mobile phone cameras. The robustness of the proposed model was tested with secondary unseen data which showed different environmental factors such as lighting, image scales, background colors and zoom levels. The results of the study may be used by public health authorities to locate mosquito vectors nearby.