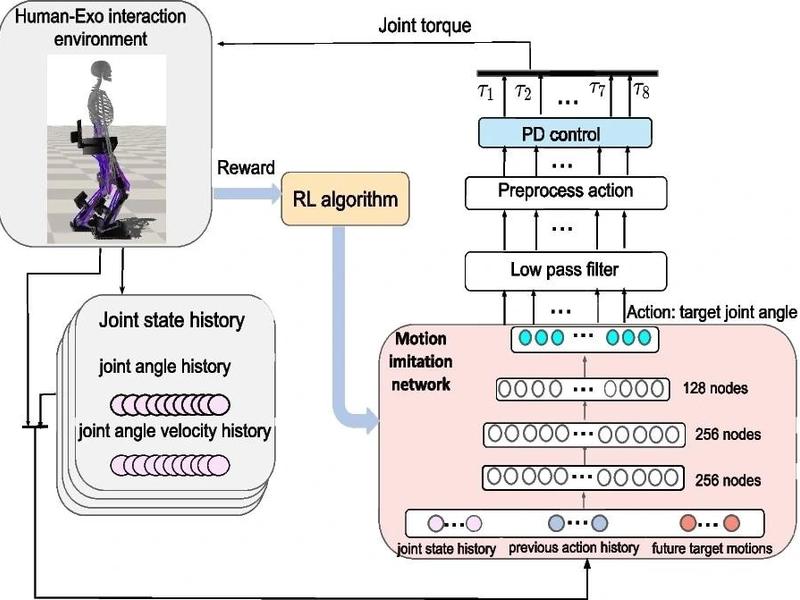
Researchers have developed a deep reinforcement learning-based controller for lower limb rehabilitation exoskeletons, which aims to assist patients with neuromuscular disorders in walking autonomously and robustly. The controller uses a decoupled simulation training technique with three independent networks to learn optimal control policies for the exoskeleton and the human, minimizing interaction forces and maintaining balance and stability.
Previous ArticleDhs Unveils Critical Infrastructure Cybersecurity Guidance
Next Article Target Makes Change At 2k Stores As Ai Rolled Out