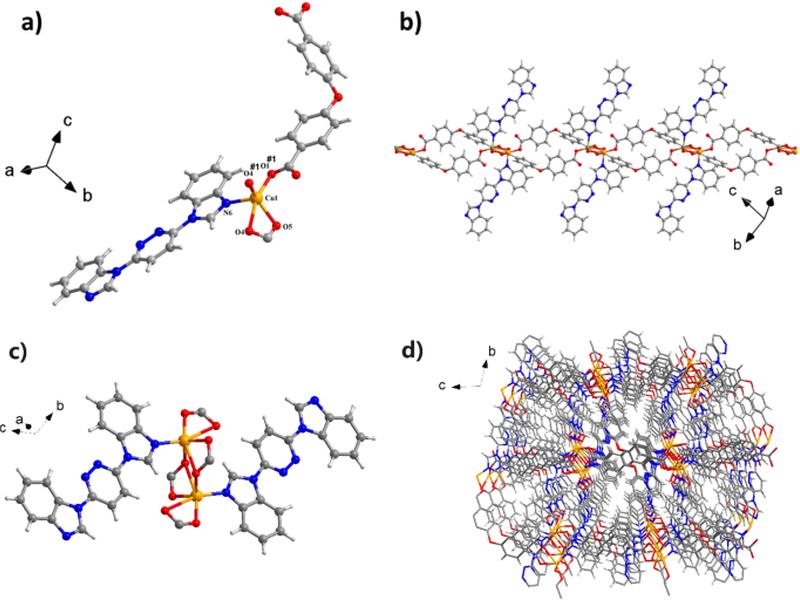
In this article, the authors discuss the use of the MolDQN algorithm for conducting reinforcement learning simulations in drug discovery. They also present the results of their simulation, which include a binding energy estimation, a synthetic availability score, and a drug similarity score. The article also includes a discussion of the crystal structure of CP1, a coordination polymer with potential applications in catalysis and gas storage.