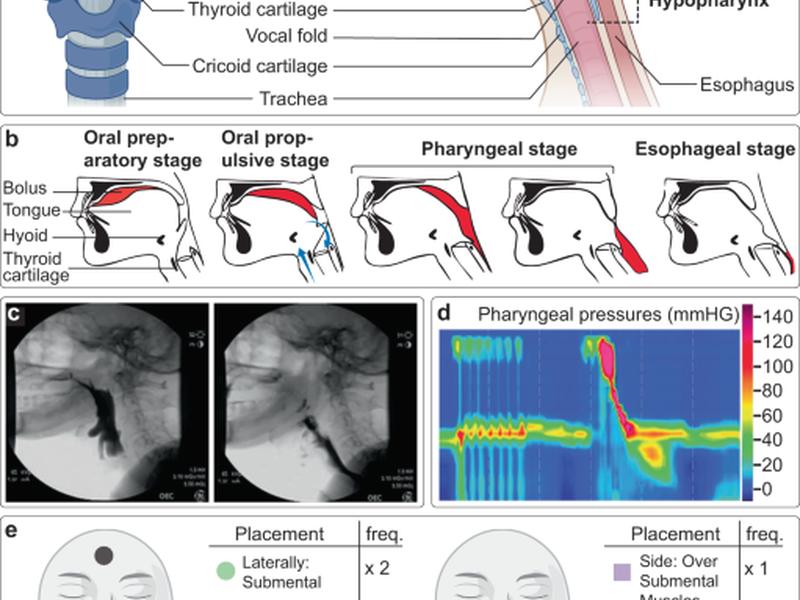
Swallowing, or deglutition, is a physiological process where the muscles of the mouth, throat, and esophagus pass food or liquid from the oral cavity to the stomach. Paradigmatic models such as four stage and process models describe the role of relevant anatomical structures in the bolus passage from the oral cavity to the esophagus. Dysphagia, or abnormal swallowing, can be caused by obstructive and damaged tissue, neurological ailments, and autoimmune diseases. A recent systematic review and meta-analysis showed that the global prevalence of oropharyngeal dysphagia is increasing, with 16.1% of the US population describing having dysphagia. Dysphagia can be managed and rehabilitated by interdisciplinary providers.