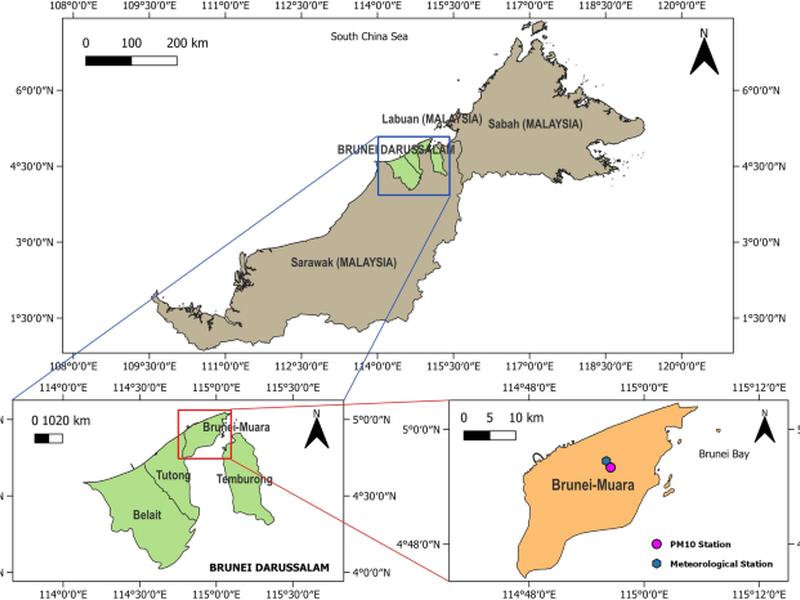
This study examines the influence of meteorological conditions on PM10 concentrations in Brunei-Muara district and the development of predictive forecasting models based on time and meteorological parameters. The incorporation of the previous day’s PM10 concentration (PM10,t-1) into the models significantly improves the models’ predictive power. The MLR model with PM10,t-1 variable shows the greatest capability in capturing the seasonal variability of daily PM10 while the RF model with PM10,t-1 variable is the most accurate for forecasting the next day’s PM10. The ANN models with PM10,t-1 variable are the most accurate for forecasting the next 2 and 3 days’ PM10. Air pollution is a global health risk, with almost all of the world’s population in 2019 living in areas where the air pollution exceeds WHO guidelines.